decode-spam-headers.py
Whether you are trying to understand why a specific e-mail ended up in SPAM/Junk for your daily Administrative duties or for your Red-Team Phishing simulation purposes, this script is there for you to help!
Idea arose while delivering a commercial Phishing Simulation exercises against MS Office365 E5 estate, equipped with MS Defender for Office365. As one can imagine, pretty tough security stack to work with from a phishing-simulation perspective. After digging manually through all these Office365 SMTP headers and trying to cherry-pick these SCL values, time come to write up a proper parser for SMTP headers.
Time went by, I was adding support for more and more SMTP headers - and here we have it. Tool that now comprehends tens of different headers.
Info
This tool accepts on input an *.EML or *.txt file with all the SMTP headers. It will then extract a subset of interesting headers and using 95+ tests will attempt to decode them as much as possible.
This script also extracts all IPv4 addresses and domain names and performs full DNS resolution of them.
Resulting output will contain useful information on why this e-mail might have been blocked.
In order to embellish your Phishing HTML code before sending it to your client, you might also want feed it into my phishing-HTML-linter.py. It does pretty decent job finding bad smells in your HTML that will get your e-mail with increased Spam-score.
Example Screenshots
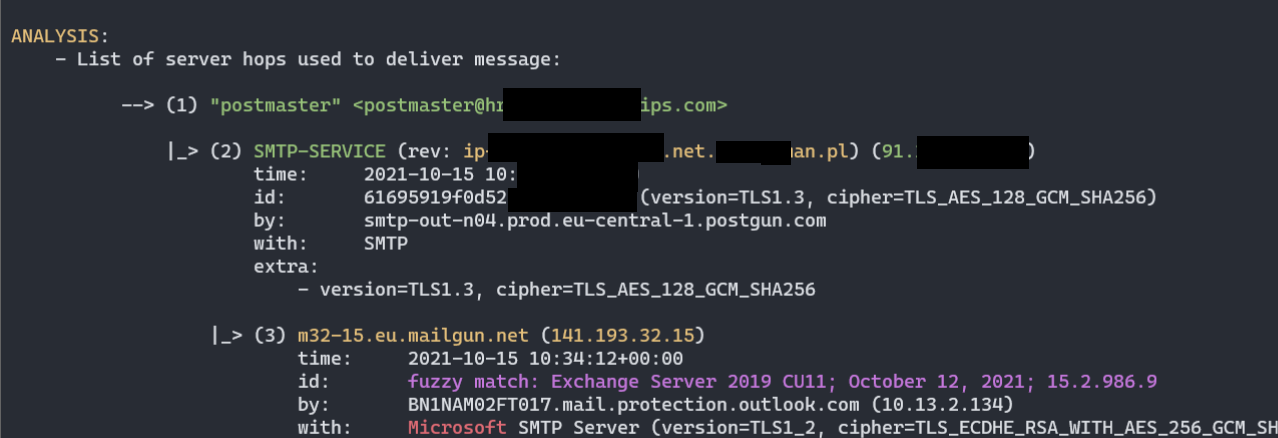
- Chain of MTA servers (nicely parsed
Receivedheaders):
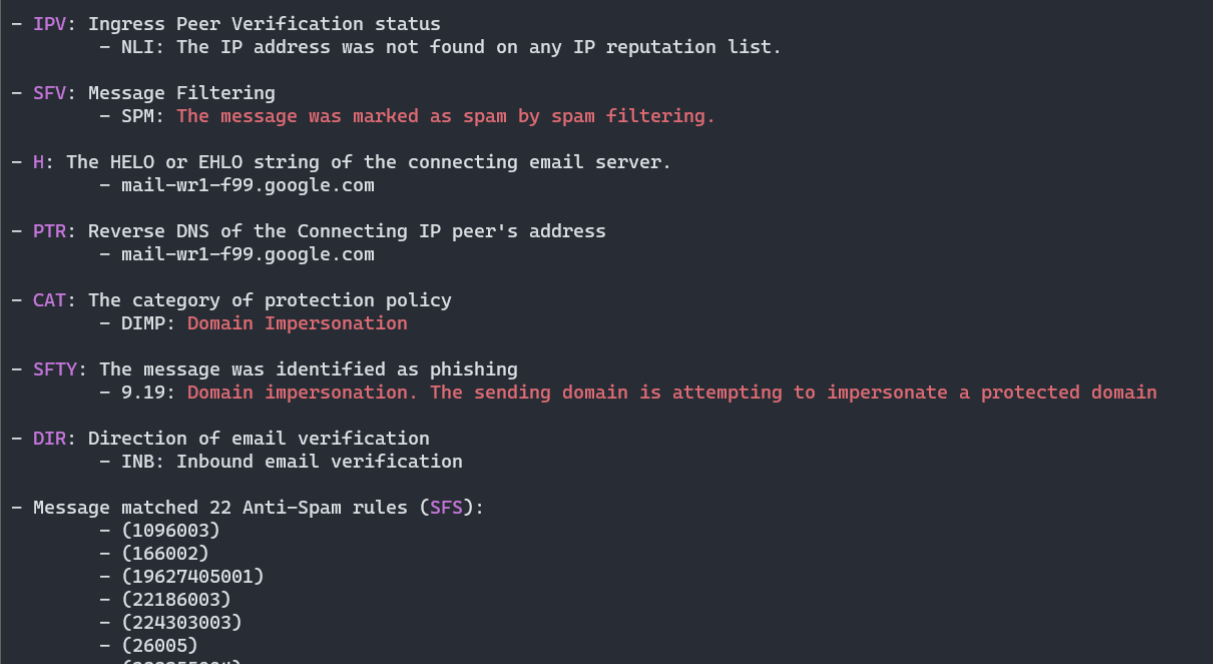
- Various headers decoded as much as possible, according to publicly available documentation (here Office365 ForeFront Spam Report):
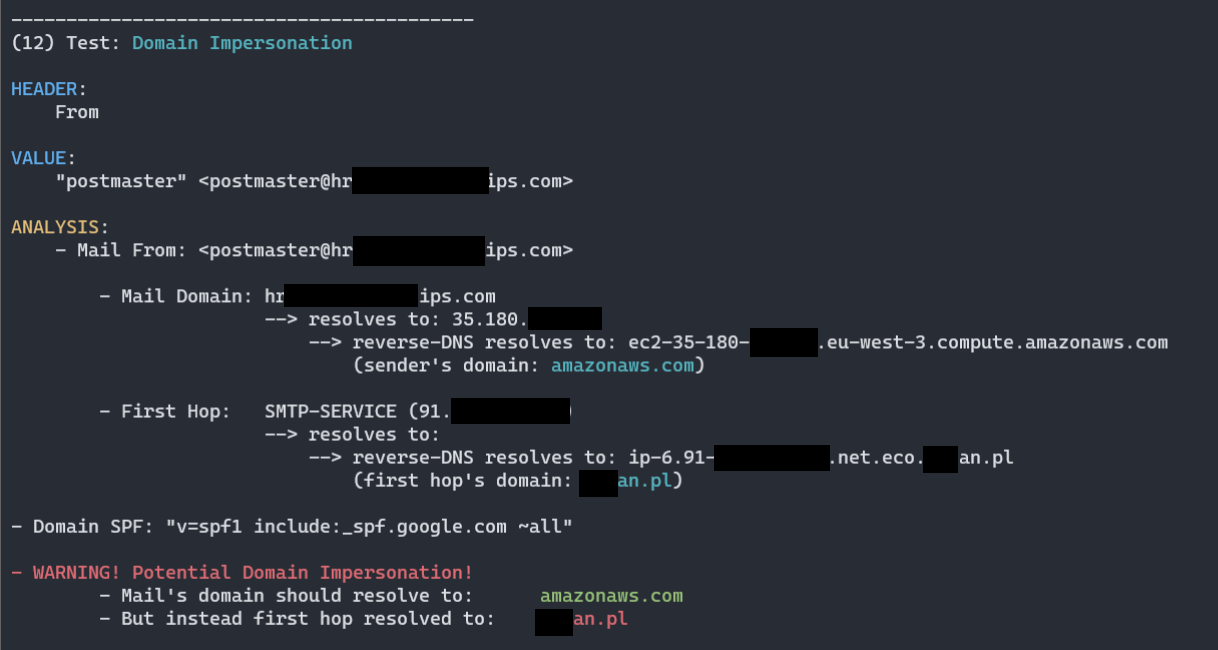
- Different custom heuristics implement to actively validate and seek for clues of spam categorization, here logic detecting Domain Impersonation:
- Script attempts to reverse-engineer and document some of the Office365 Anti-Spam rules, as well as collect public knowledge about other opaque Anti-Spam headers:
Processed headers
Processed headers (more than 76+ headers are parsed):
X-forefront-antispam-reportX-exchange-antispamX-exchange-antispam-mailbox-deliveryX-exchange-antispam-message-infoX-microsoft-antispam-report-cfa-testReceivedFromToSubjectThread-topicReceived-spfX-mailerX-originating-ipUser-agentX-forefront-antispam-reportX-microsoft-antispam-mailbox-deliveryX-microsoft-antispamX-exchange-antispam-report-cfa-testX-spam-statusX-spam-levelX-spam-flagX-spam-reportX-vr-spamcauseX-ovh-spam-reasonX-vr-spamscoreX-virus-scannedX-spam-checker-versionX-ironport-avX-ironport-anti-spam-filteredX-ironport-anti-spam-resultX-mimecast-spam-scoreSpamdiagnosticmetadataX-ms-exchange-atpmessagepropertiesX-msfblX-ms-exchange-transport-endtoendlatencyX-ms-oob-tlc-oobclassifiersX-ip-spam-verdictX-amp-resultX-ironport-remoteipX-ironport-reputationX-sbrsX-ironport-sendergroupX-policyX-ironport-mailflowpolicyX-remote-ipX-sea-spamX-fireeyeX-antiabuseX-tmase-versionX-tm-as-product-verX-tm-as-resultX-imss-scan-detailsX-tm-as-user-approved-senderX-tm-as-user-blocked-senderX-tmase-resultX-tmase-snap-resultX-imss-dkim-white-listX-tm-as-result-xfilterX-tm-as-smtpX-scanned-byX-mimecast-spam-signatureX-mimecast-bulk-signatureX-sender-ipX-forefront-antispam-report-untrustedX-microsoft-antispam-untrustedX-sophos-senderhistoryX-sophos-rescanX-MS-Exchange-CrossTenant-IdX-OriginatorOrgIronPort-DataIronPort-HdrOrdrX-DKIMDKIM-FilterX-SpamExperts-ClassX-SpamExperts-EvidenceX-Recommended-ActionX-AppInfo
Most of these headers are not fully documented, therefore the script is unable to pinpoint all the details, but at least it collects all I could find on them.
Reverse-Engineering efforts
I'm making signifcant efforts to spot and understand different Office365 ForeFront Anti-Spam ruls (SFS, ENG) despite them not being publicly documented.
------------------------------------------
(5) Test: X-Forefront-Antispam-Report
HEADER:
X-Forefront-Antispam-Report
VALUE:
CIP:209.85.167.100;CTRY:US;LANG:de;SCL:5;SRV:;IPV:NLI;SFV:SPM;H:mail-lf1-f100.google.com;PTR:mail-l
f1-f100.google.com;CAT:DIMP;SFTY:9.19;SFS:(4636009)(956004)(166002)(6916009)(356005)(336012)(19
625305002)(22186003)(5660300002)(4744005)(6666004)(35100500006)(82960400001)(26005)(7596003)(7636003)(554460
02)(224303003)(1096003)(58800400005)(86362001)(9686003)(43540500002);DIR:INB;SFTY:9.19;
[...]
- Message matched 24 Anti-Spam rules (SFS): <============ opaque anti-spam rules
- (1096003)
- (166002)
- (19625305002)
- (22186003)
- (224303003)
- (26005)
- (336012)
- (356005)
- (35100500006) - (SPAM) Message contained embedded image.
The process is purely manual and resorts to sending specifically designed mails to the Office365 mail servers and then manually reviewing and correlating collected rules.
Having sent more than 60 mails already, this is what I can tell by now about Microsoft's rules:
#
# Below rules were collected solely in a trial-and-error manner or by scraping any
# pieces of information from all around the Internet.
#
# They do not represent the actual Anti-Spam rule name or context and surely represent
# something close to what is understood (or they may have totally different meaning).
#
# Until we'll be able to review anti-spam rules documention, there is no viable mean to map
# rule ID to its meaning.
#
Anti_Spam_Rules_ReverseEngineered = \
{
'35100500006' : logger.colored('(SPAM) Message contained embedded image.', 'red'),
# https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/416100/what-is-meanings-of-39x-microsoft-antispam-mailbox.html
'520007050' : logger.colored('(SPAM) Moved message to Spam and created Email Rule to move messages from this particular sender to Junk.', 'red'),
# triggered on an empty mail with subject being: "test123 - viagra"
'162623004' : 'Subject line contained suspicious words (like Viagra).',
# triggered on mail with subject "test123" and body being single word "viagra"
'19618925003' : 'Mail body contained suspicious words (like Viagra).',
# triggered on mail with empty body and subject "Click here"
'28233001' : 'Subject line contained suspicious words luring action (ex. "Click here"). ',
# triggered on a mail with test subject and 1500 words of http://nietzsche-ipsum.com/
'30864003' : 'Mail body contained a lot of text (more than 10.000 characters).',
# mails that had simple message such as "Hello world" triggered this rule, whereas mails with
# more than 150 words did not.
'564344004' : 'HTML mail body with less than 150 words of text (not sure how much less though)',
# message was sent with a basic html and only one <u> tag in body.
'67856001' : 'HTML mail body contained underline <u> tag.',
# message with html,head,body and body containing simple text with no b/i/u formatting.
'579124003' : 'HTML mail body contained text, but no text formatting (<b>, <i>, <u>) was present',
# This is a strong signal. Mails without <a> doesnt have this rule.
'166002' : 'HTML mail body contained URL <a> link.',
# Message contained <a href="https://something.com/file.html?parameter=value" - GET parameter with value.
'21615005' : 'Mail body contained <a> tag with URL containing GET parameter: ex. href="https://foo.bar/file?aaa=bbb"',
# Message contained <a href="https://something.com/file.html?parameter=https://another.com/website"
# - GET parameter with value, being a URL to another website
'45080400002' : 'Something about <a> tag\'s URL. Possibly it contained GET parameter with value of another URL: ex. href="https://foo.bar/file?aaa=https://baz.xyz/"',
# Message contained <a> with href pointing to a file with dangerous extension, such as file.exe
'460985005' : 'Mail body contained HTML <a> tag with href URL pointing to a file with dangerous extension (such as .exe)',
#
# Message1: GoPhish -> VPS 587/tcp redirector -> smtp.gmail.com:587 -> target
# Message2: GoPhish -> VPS 587/tcp redirector -> smtp-relay.gmail.com:587 -> target
#
# These were the only differences I spotted:
# Message1 - FirstHop Gmail SMTP Received with ESMTPS.
# Message2 - FirstHop Gmail SMTP-Relay Received with ESMTPSA.
#
'121216002' : 'First Hop MTA SMTP Server used as a SMTP Relay. It\'s known to originate e-mails, but here it acted as a Relay. Or maybe due to use of "with ESMTPSA" instead of ESMTPS?',
# Triggered on message with <a> added to HTML: <a href="https://support.spotify.com/is-en/">https://www.reddit.com/</a>
'966005' : 'Mail body contained link tag with potentially masqueraded URL: <a href="https://attacker.com">https://example.com</a>',
#
# Message1: GoPhish EC2 -> another EC2 with socat to smtp.gmail.com:587 (authenticated) -> Target
# Message2: GoPhish EC2 -> Gsuite -> Target
#
# Subject, mail body were exactly the same.
#
# Below two rules were added to the second message. My understanding is that they're somehow referring
# to the reputation of the first-hop server, maybe reverse-DNS resolution.
#
'5002400100002' : "(GUESSING) Somehow related to First Hop server reputation, it's reverse-PTR resolution or domain impersonation",
'58800400005' : "(GUESSING) Somehow related to First Hop server reputation, it's reverse-PTR resolution or domain impersonation",
'19625305002' : '(GUESSING) Something to do with the HTML code and used tags/structures',
'43540500002' : '(GUESSING) Something to do with the HTML code and used tags/structures',
'460985005' : '(GUESSING) Something to do with either more-complex HTML code or with the <a> tag and its URL.',
# Triggered on an empty text message, subject "test" - that was marked with "Domain Impersonation", however
# ForeFront Anti-Spam headers did not support that Domain Impersonation. Weird.
'22186003' : '(GUESSING) Something to do with either Text message (non-HTML) or probable Domain Impersonation'
}
Should you know anything about any other Office365 anti-spam rules (or have suggestions to the ones described above) - let me know in this repo's issues, I'll add it straight away :)
Usage
Help:
PS> py .\decode-spam-headers.py --help
usage: decode-spam-headers.py [options] <file>
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
Required arguments:
infile Input file to be analysed or --list tests to show available tests.
Options:
-o OUTFILE, --outfile OUTFILE
Output file with report
-f {json,text}, --format {json,text}
Analysis report format. JSON, text. Default: text
-N, --nocolor Dont use colors in text output.
-v, --verbose Verbose mode.
-d, --debug Debug mode.
-l, --list List available tests and quit. Use it like so: --list tests
Tests:
-i tests, --include-tests tests
Comma-separated list of test IDs to run. Ex. --include-tests 1,3,7
-e tests, --exclude-tests tests
Comma-separated list of test IDs to skip. Ex. --exclude-tests 1,3,7
-r, --resolve Resolve IPv4 addresses / Domain names.
-a, --decode-all Decode all =?us-ascii?Q? mail encoded messages and print their contents.
If you want to run only a subset of tests, you'll first need to learn Test IDs of which to pick.
Run the script with -l tests to grab that list.
List available test and their corresponding IDs:
C:\> py decode-spam-headers.py -l tests
[.] Available tests:
TEST_ID - TEST_NAME
--------------------------------------
1 - Received - Mail Servers Flow
2 - Extracted IP addresses
3 - Extracted Domains
4 - Bad Keywords In Headers
5 - From Address Analysis
6 - Subject and Thread Topic Difference
7 - Authentication-Results
8 - ARC-Authentication-Results
9 - Received-SPF
10 - Mail Client Version
11 - User-Agent Version
12 - X-Forefront-Antispam-Report
13 - X-MS-Exchange-Organization-SCL
14 - X-Microsoft-Antispam-Mailbox-Delivery
15 - X-Microsoft-Antispam Bulk Mail
16 - X-Exchange-Antispam-Report-CFA-Test
17 - Domain Impersonation
18 - SpamAssassin Spam Status
19 - SpamAssassin Spam Level
20 - SpamAssassin Spam Flag
21 - SpamAssassin Spam Report
22 - OVH's X-VR-SPAMCAUSE
23 - OVH's X-Ovh-Spam-Reason
24 - OVH's X-Ovh-Spam-Score
25 - X-Virus-Scan
26 - X-Spam-Checker-Version
27 - X-IronPort-AV
28 - X-IronPort-Anti-Spam-Filtered
29 - X-IronPort-Anti-Spam-Result
30 - X-Mimecast-Spam-Score
31 - Spam Diagnostics Metadata
32 - MS Defender ATP Message Properties
33 - Message Feedback Loop
34 - End-to-End Latency - Message Delivery Time
35 - X-MS-Oob-TLC-OOBClassifiers
36 - X-IP-Spam-Verdict
37 - X-Amp-Result
38 - X-IronPort-RemoteIP
39 - X-IronPort-Reputation
40 - X-SBRS
41 - X-IronPort-SenderGroup
42 - X-Policy
43 - X-IronPort-MailFlowPolicy
44 - X-SEA-Spam
45 - X-FireEye
46 - X-AntiAbuse
47 - X-TMASE-Version
48 - X-TM-AS-Product-Ver
49 - X-TM-AS-Result
50 - X-IMSS-Scan-Details
51 - X-TM-AS-User-Approved-Sender
52 - X-TM-AS-User-Blocked-Sender
53 - X-TMASE-Result
54 - X-TMASE-SNAP-Result
55 - X-IMSS-DKIM-White-List
56 - X-TM-AS-Result-Xfilter
57 - X-TM-AS-SMTP
58 - X-TMASE-SNAP-Result
59 - X-TM-Authentication-Results
60 - X-Scanned-By
61 - X-Mimecast-Spam-Signature
62 - X-Mimecast-Bulk-Signature
63 - X-Forefront-Antispam-Report-Untrusted
64 - X-Microsoft-Antispam-Untrusted
65 - X-Mimecast-Impersonation-Protect
66 - X-Proofpoint-Spam-Details
67 - X-Proofpoint-Virus-Version
68 - SPFCheck
69 - X-Barracuda-Spam-Score
70 - X-Barracuda-Spam-Status
71 - X-Barracuda-Spam-Report
72 - X-Barracuda-Bayes
73 - X-Barracuda-Start-Time
74 - Similar to SpamAssassin Spam Level headers
75 - SMTP Header Contained IP address
76 - Other unrecognized Spam Related Headers
77 - Other interesting headers
78 - Security Appliances Spotted
79 - Email Providers Infrastructure Clues
80 - X-Microsoft-Antispam-Message-Info (use -a to show its results)
81 - Decoded Mail-encoded header values (use -a to show its results)
82 - Header Containing Client IP
83 - Office365 Tenant ID
84 - Organization Name
85 - MS Defender For Office365 Safe Links Version
86 - Suspicious Words in Headers
87 - AWS SES Outgoing
88 - IronPort-Data
89 - IronPort-HdrOrder
90 - X-DKIM
91 - DKIM-Filter
92 - X-SpamExperts-Class
93 - X-SpamExperts-Evidence
94 - X-Recommended-Action
95 - X-AppInfo
Sample run
Sample run (output structure and contents come from an outdated version of the script):
PS> py decode-spam-headers.py headers.txt
------------------------------------------
(1) Test: Received - Mail Servers Flow
HEADER:
Received
VALUE:
...
ANALYSIS:
- List of server hops used to deliver message:
--> (1) "attacker" <attacker@attacker.com>
|_> (2) SMTP-SERVICE (44.55.66.77)
time: 01 Jan 2021 12:34:20
|_> (3) mail-wr1-f51.google.com (209.85.221.51)
time: 01 Jan 2021 12:34:20
version: fuzzy match: Exchange Server 2019 CU11; October 12, 2021; 15.2.986.9
|_> (4) SN1NAM02FT0061.eop-nam02.prod.protection.outlook.com (2603:10b6:806:131:cafe::e5)
time: 01 Jan 2021 12:34:20
version: fuzzy match: Exchange Server 2019 CU11; October 12, 2021; 15.2.986.9
|_> (5) SA0PR11CA0138.namprd11.prod.outlook.com (2603:10b6:806:131::23)
time: 01 Jan 2021 12:34:20
version: fuzzy match: Exchange Server 2019 CU11; October 12, 2021; 15.2.986.9
|_> (6) CP2PR80MB4114.lamprd80.prod.outlook.com (2603:10d6:102:3c::15)
time: 01 Jan 2021 12:34:23
|_> (7) "Victim Surname" <victim@contoso.com>
------------------------------------------
[...]
------------------------------------------
(4) Test: Mail Client Version
HEADER:
X-Mailer
VALUE:
OEM
ANALYSIS:
- X-Mailer header was present and contained value: "OEM".
------------------------------------------
(5) Test: X-Forefront-Antispam-Report
HEADER:
X-Forefront-Antispam-Report
VALUE:
CIP:209.85.167.100;CTRY:US;LANG:de;SCL:5;SRV:;IPV:NLI;SFV:SPM;H:mail-lf1-f100.google.com;PTR:mail-l
f1-f100.google.com;CAT:DIMP;SFTY:9.19;SFS:(4636009)(956004)(166002)(6916009)(356005)(336012)(19
625305002)(22186003)(5660300002)(4744005)(6666004)(35100500006)(82960400001)(26005)(7596003)(7636003)(554460
02)(224303003)(1096003)(58800400005)(86362001)(9686003)(43540500002);DIR:INB;SFTY:9.19;
ANALYSIS:
- Microsoft Office365/Exchange ForeFront Anti-Spam report
- CIP: Connecting IP address: 209.85.167.100
- CTRY: The source country as determined by the connecting IP address
- US
- LANG: The language in which the message was written
- de
- IPV: Ingress Peer Verification status
- NLI: The IP address was not found on any IP reputation list.
- SFV: Message Filtering
- SPM: The message was marked as spam by spam filtering.
- H: The HELO or EHLO string of the connecting email server.
- mail-lf1-f100.google.com
- PTR: Reverse DNS of the Connecting IP peer's address
- mail-lf1-f100.google.com
- CAT: The category of protection policy
- DIMP: Domain Impersonation
- SFTY: The message was identified as phishing
- 9.19: Domain impersonation. The sending domain is attempting to impersonate a protected domain
- DIR: Direction of email verification
- INB: Inbound email verification
- Message matched 24 Anti-Spam rules (SFS):
- (1096003)
- (166002)
- (19625305002)
- (22186003)
- (224303003)
- (26005)
- (336012)
- (356005)
- (35100500006) - (SPAM) Message contained embedded image.
- (43540500002)
- (4636009)
- (4744005)
- (55446002)
- (5660300002)
- (58800400005)
- (6666004)
- (6916009)
- (7596003)
- (7636003)
- (82960400001)
- (86362001)
- (956004)
- (9686003)
- SCL: Spam Confidence Level: 5
- SPAM: Spam filtering marked the message as Spam
More information:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/office-365-security/anti-spam-message-headers
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/antispam-and-antimalware/antispam-protection/antispam-stamps
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/office-365-security/spam-confidence-levels
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/exchange/monitoring/trace-an-email-message/run-a-message-trace-and-view-results
------------------------------------------
(6) Test: X-Microsoft-Antispam-Mailbox-Delivery
HEADER:
X-Microsoft-Antispam-Mailbox-Delivery
VALUE:
ucf:0;jmr:1;auth:0;dest:J;ENG:(910001)(944506458)(944626604)(750132)(520011016);
ANALYSIS:
- This header denotes what to do with received message, where to put it.
- auth: Message originating from Authenticated sender
- 0: Not Authenticated
- dest: Destination where message should be placed
- J: JUNK directory
- Message matched 6 Anti-Spam Delivery rules:
- (520011016)
- (750132)
- (910001)
- (944506458)
- (944626604)
------------------------------------------
(7) Test: X-Microsoft-Antispam Bulk Mail
HEADER:
X-Microsoft-Antispam
VALUE:
BCL:0;
ANALYSIS:
- BCL: BULK Confidence Level: 0
The message isn't from a bulk sender.
More information:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/microsoft-365/security/office-365-security/bulk-complaint-level-values
------------------------------------------
[...]
------------------------------------------
(10) Test: MS Defender ATP Message Properties
HEADER:
X-MS-Exchange-AtpMessageProperties
VALUE:
SA|SL
ANALYSIS:
- MS Defender Advanced Threat Protection enabled following protections on this message:
- Safe Attachments Protection
- Safe Links Protection
------------------------------------------
(11) Test: Domain Impersonation
HEADER:
From
VALUE:
"attacker" <attacker@attacker.com>
ANALYSIS:
- Mail From: <attacker@attacker.com>
- Mail Domain: attacker.com
--> resolves to: 11.22.33.44
--> reverse-DNS resolves to: ec2-11-22-33-44.eu-west-3.compute.amazonaws.com
(sender's domain: amazonaws.com)
- First Hop: SMTP-SERVICE (44.55.66.77)
--> resolves to:
--> reverse-DNS resolves to: host44-55-66-77.static.arubacloud.pl
(first hop's domain: arubacloud.pl)
- Domain SPF: "v=spf1 include:_spf.google.com ~all"
- WARNING! Potential Domain Impersonation!
- Mail's domain should resolve to: amazonaws.com
- But instead first hop resolved to: arubacloud.pl
☕ Show Support ☕
This and other projects are outcome of sleepless nights and plenty of hard work. If you like what I do and appreciate that I always give back to the community, Consider buying me a coffee (or better a beer) just to say thank you! 💪
Mariusz Banach / mgeeky, (@mariuszbit)
<mb [at] binary-offensive.com>